There are many decisions you must make regarding payroll. A basic one—which type of pay period you’ll choose—may seem simple on the surface but is more complex when you consider payroll compliance, cash flow, and employee morale.
Below is foundational knowledge to help you understand pay periods, the different types, and how to choose one so you can make the best decision for your company, finance team, and employees.
What is a Pay Period?
A pay period is a recurring schedule that determines how often employees get paid. In other words, it’s the time frame for tracking employee work hours and calculating wages.
Common pay periods include weekly, biweekly, semimonthly, and monthly, each with its own set of pros and cons. The choice of pay period can significantly impact the company’s cash flow, payroll process, and the employees’ financial well-being, making it a crucial decision for any organization.
Pay Period vs. Pay Date
While a pay period refers to the period during which work is performed, the pay date is the actual day employees receive their paychecks. These two terms are closely related but represent different aspects of the payroll process.
The pay period defines the time frame for which wages are calculated, such as the first to the 15th of the month or from Monday to Sunday. Once the pay period ends, employers need time to calculate hours worked, apply taxes, and make any necessary deductions. This processing leads to the pay date, which is when the funds are distributed to employees.
For example, if your pay period runs from the 1st to the 15th, the pay date might be on the 20th, giving the payroll team a few days to process everything. The gap between the end of the pay period and the pay date is crucial for ensuring accuracy and compliance with payroll laws.
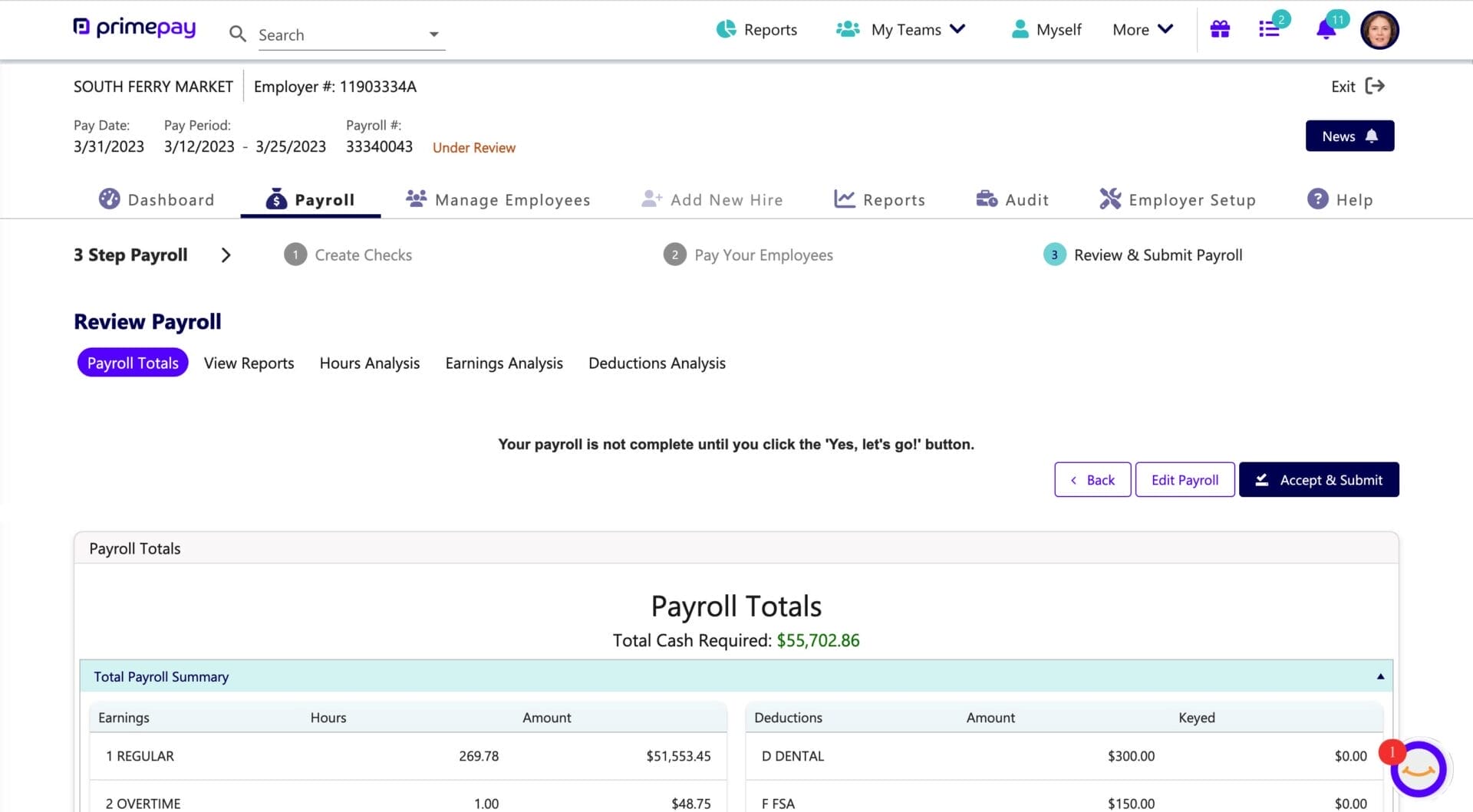
As you can see above, the pay period ended on 3/25, but the pay date isn’t until 3/31, which means the payment has accrued.
Types of Pay Periods
Choosing the right pay schedule for your business involves understanding the different types available and how each can affect your operations and employees.
As of 2023, 43% of U.S. private companies opt for biweekly pay periods, meaning employees receive paychecks every two weeks. However, the best pay period for your company will depend on various factors, including your industry, cash flow, and employee preferences.
Here’s a breakdown of the most common pay periods:
Weekly
With a weekly pay period, employees are paid once every week, typically on the same day (like every Friday). This option is popular in industries where employees work hourly, such as construction, retail, and hospitality. The advantage of weekly pay is that it provides employees with more frequent cash flow, which can be especially beneficial for those who rely on a steady income. However, it also means more frequent payroll processing, which can be time-consuming and costly for employers.
Bi-Weekly
Bi-weekly pay periods occur every two weeks, meaning employees receive 26 paychecks per year. This option is one of the most common pay schedules, balancing the need for regular employee compensation with less frequent payroll processing compared to weekly pay. Bi-weekly pay is popular in various industries and works well for both salaried and hourly employees. It also simplifies overtime calculations since each pay period usually includes precisely two weeks.
Semi-Monthly
With a semi-monthly pay period, employees are paid twice a month, often on the 1st and the 15th, or the 15th and the last day of the month. This results in 24 pay periods per year. Semi-monthly pay is often used for salaried employees and can be simpler for employers when dealing with monthly expenses and budget planning. However, it can be trickier to calculate overtime for hourly employees, as the pay periods don’t always align neatly with the calendar weeks.
Monthly
Monthly pay periods mean employees are paid once a month, usually on the same date each month. While this is less common in the U.S., it’s used in some industries, particularly for higher-level salaried positions. Monthly payrolls are easier to manage from an administrative perspective since they only require processing once per month. Still, they can create financial strain for employees who need to budget carefully between paychecks.
On-Demand
On-demand pay, also known as earned wage access, allows employees to access a portion of their earned wages before the standard payday. This option is becoming increasingly popular as a way to offer employees more flexibility and financial security, especially since 58% of Americans live paycheck to paycheck. However, it requires employers to have systems in place to manage these requests without disrupting regular payroll processes.
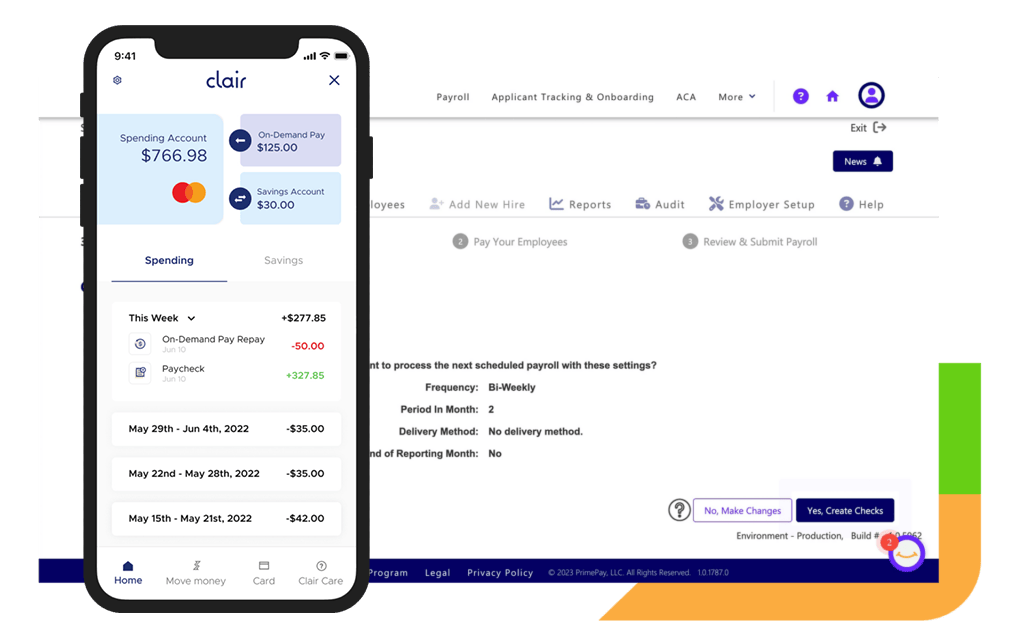
PrimePay’s On-Demand pay feature offers financial benefits to employees – at no cost or lift to clients.
How to Choose a Pay Period
Selecting a pay schedule for your business is a crucial decision that impacts your payroll process, cash flow, and employee satisfaction.
Here are some factors to consider:
- Employee preferences: Understanding your employees’ needs and preferences is essential. For example, hourly workers might appreciate the steady income of weekly or bi-weekly pay, while salaried employees might be fine with semi-monthly or monthly schedules. Gathering employees’ insights or discussing options with your team can provide valuable data.
- Industry norms: Look at what’s standard in your industry. Due to the hourly nature of work in sectors like retail or hospitality, weekly or bi-weekly pay periods are common. In contrast, industries with primarily salaried employees might lean towards semi-monthly or monthly pay periods. Aligning with industry norms can make your business more attractive to potential hires.
- Cash flow management: Consider your company’s cash flow when selecting a pay period. More frequent pay periods, like weekly or bi-weekly, mean you’ll need funds available more often. On the other hand, monthly pay periods allow more time to manage finances but may require careful planning to ensure you can meet payroll commitments on time.
- Legal requirements: Ensure that your chosen pay period complies with state and federal regulations. Some states have specific requirements regarding how often employees must be paid, particularly for hourly employees. It’s crucial to familiarize yourself with these laws to avoid penalties and ensure your payroll practices are compliant.
- Flexibility and technology: With the rise of on-demand pay and advanced payroll software, offering flexible pay options is easier than ever. If your company uses modern payroll technology, you might be able to offer employees multiple pay period options or even on-demand pay, providing greater flexibility and satisfaction.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose a pay period that supports your business’s financial health, keeps your payroll process efficient, and meets the needs of your employees.


