It’s safe to say that winter brings a flurry of activity (wink wink). From managing employee PTO requests to conducting performance reviews to closing the books, it’s no wonder HBR refers to this time of year as the “December deadline deluge.”
And that last piece – closing the books and handling your end-of-year reporting – can be a doozy. That’s because HR and payroll teams must prepare for the year’s end, comply with tax laws, and plan for the next annual payroll.
A great way to make sure you’ve crossed all your t’s and dotted your i’s is to follow a payroll checklist. By following a year-end payroll checklist, you can better track employee pay, manage deductions, and review payroll data. The results? Your business remains compliant, employees are paid accurately, and tax obligations are met.
Grab your free year-end payroll checklist to stay on track through the new year.
1. Prepare for Year-End Payroll
To prepare for your year-end payroll, there are three primary steps to complete including data verification, payroll provider coordination, and fringe benefits reporting.
We will cover each of these in more detail below.
Verify Employee and Contractor Information
In the best-case scenario, you’ve maintained accurate employee and contractor information throughout the year. Doing so will make your Q4 smooth sailing and ideally prevent expensive delays and penalties with tax authorities.
If you’re not up-to-date, make sure you:
- Confirm employee data, including full names, social security numbers, addresses, and other essential details.
- Verify contractors’ tax ID numbers using Form W-9.
- Update your records if discrepancies are identified.
- Inform your payroll service provider of any modifications.
TIP: Store your payroll records and tax forms for at least four years to stay compliant with legal obligations and avoid potential penalties. It’s also good to store these records digitally for easy access and streamlined record-keeping.
Coordinate with Your Payroll Provider
Maintaining an open dialogue with your payroll provider aids in accurate year-end payroll processing, prevents delays, and helps avoid expensive errors. Contact your payroll provider before the last payroll of the calendar year to discuss the following:
- Processing the final payroll.
- Any pay date changes due to holidays.
- Tax withholdings, employee contributions, and other essential payroll adjustments.
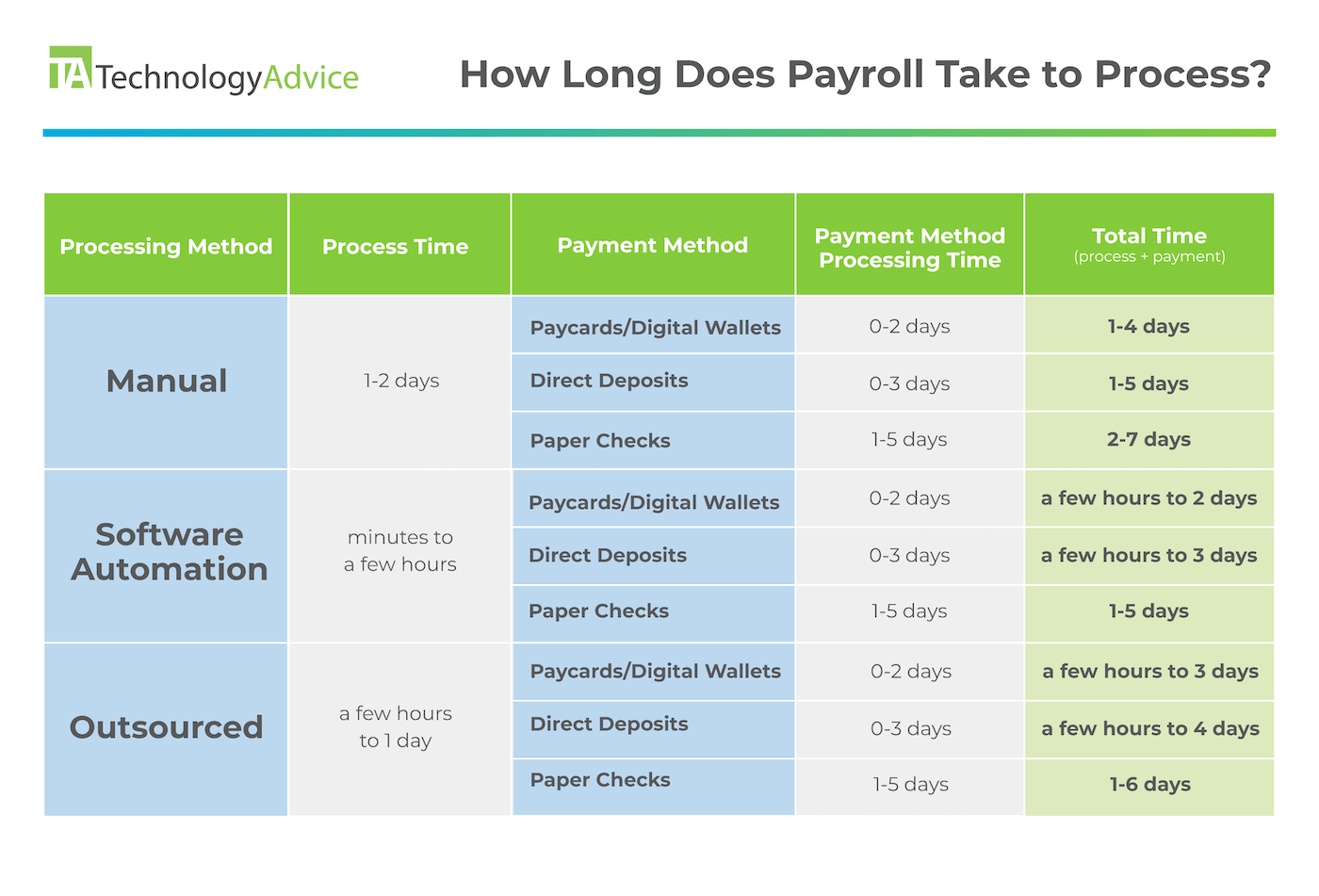
When processing year-end payroll, consider the processing time and method to ensure you hit deadlines and pay your people in a timely manner.
Manage Fringe Benefits and Third-Party Payouts
Maintaining compliance and avoiding potential tax penalties requires accurately reporting fringe benefits and third-party payouts.
- Submit fringe benefits – such as health insurance coverage and retirement contributions – to your payroll provider no later than your last scheduled payroll of the year.
- Report the fair market value of these benefits on the employee’s W-2 form, ensuring all tax liabilities are accounted for.
- Provide details of any third-party disability payments to your payroll provider.
After running the final payroll of the year, verify that all employee wages and deductions are accurate before reporting on the W-2 form.
2. Navigate State Reporting Requirements
Each state has its rules and regulations, making handling state reporting requirements a bit of a mess if your employees are dispersed.
- Wage-and-hour requirements
- Withholding and tax reporting
- Unemployment tax reporting
- Specific local regulations
The differences between states are vast and varied, so you must familiarize yourself with the specific requirements of each state you operate in.
However, ignoring these requirements can lead to severe consequences, including financial penalties, interest charges, and potential legal repercussions.
State-Specific Regulations
State-specific regulations can be as varied as the landscapes of the states themselves. Take California, for example. Employers with 100 or more employees have to report pay and hours worked data by establishment, and all employers have to report new or rehired employees to the New Employee Registry within 20 days of their employment. In addition to these state-specific regulations, employers must comply with the Fair Labor Standards Act and relevant labor laws.
Meanwhile, in Texas, there are distinct state payroll tax forms that employers can access on the official website of the Texas Comptroller of Public Accounts. Think of it as each state having its own unique guidebook that employers must understand and follow.
TIP: Keep your state information in one place for quick reference and up-to-date resources. Or, bookmark our Wage and Tax Resources for a convenient one-stop-shop of federal and state-specific information.
Tax Compliance Strategies
With each state having its rulebook, it’s crucial to have a game plan for compliance. Some strategies to employ include:
- Registering with the appropriate state government.
- Ensuring accurate calculation and withholding of federal and state payroll taxes.
- Reporting these taxes to the relevant government agencies.
But remember, failing to comply with state payroll reporting requirements can lead to severe consequences, including late fees, interest charges, fines, and, in certain instances, felony charges and imprisonment.
3. Distribute W-2 and 1099 Forms to Your Employees and Contractors
Business owners must complete and distribute W-2 and 1099 forms to employees and contractors by January 31. These forms report the employee’s wages, tax withholdings, and other essential payroll information for the calendar year.
Once you’ve provided W-2 and 1099 forms to your employees, submit them to the appropriate tax authorities, such as the SSA and IRS. Submitting these forms on time is necessary to prevent penalties and remain compliant with federal and state tax laws.
For independent contractors, you must send Form 1099, which documents payments for services provided during a specific pay period. It’s a crucial step in reporting any amount of federal income and fulfilling tax reporting obligations.
However, this form comes with its own set of details. You need to have the contractor’s name and address, their taxpayer identification number (TIN), and the total amount paid to the contractor during the tax year. Consider it a to-do list to complete before handing out Form 1099.
Again, you must distribute both electronic and paper records of W-2s and 1099s by January 31. Delayed distribution can result in penalties ranging from $60 to $310 per form, a price you don’t want to pay.
TIP: If the worst-case scenario occurs – you forget to file or have incorrect W-2s – there are steps to take to mitigate the damage (unfortunately, building a time machine isn’t one of them).
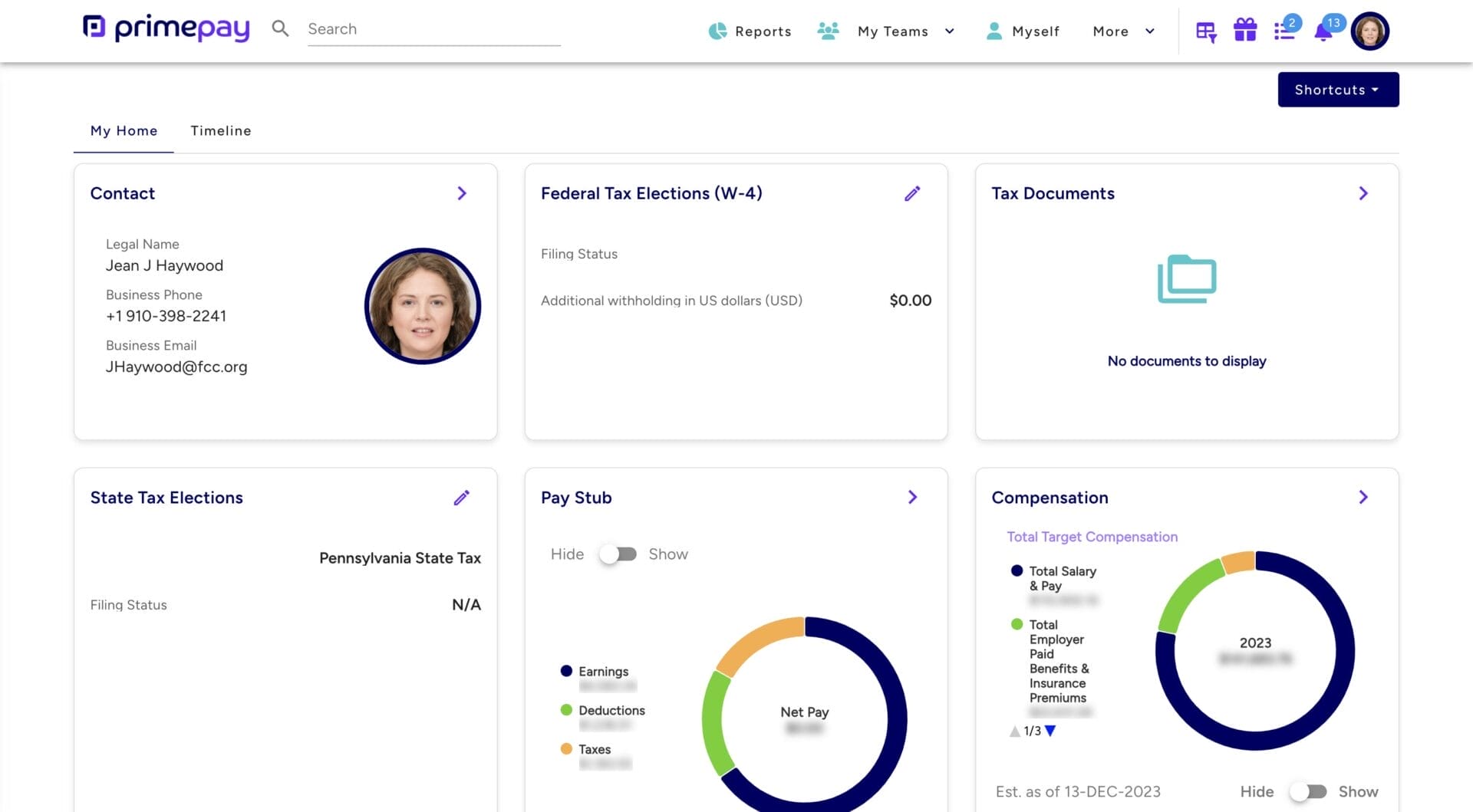
Using an employee self-service portal allows employees to update their information and see tax documents in one place.
4. Meet Deadlines and Maintain Compliance
An integral part of your year-end payroll checklist is staying versed on essential payroll forms and deadlines. In short, your business must complete, file, and submit applicable payroll tax forms to the IRS, SSA, state tax authorities, and other relevant entities.
Tax Forms and Filing Deadlines
Staying informed about tax forms and filing deadlines is essential for any business, especially in Q4. In addition to W-2 and 1099 forms, companies must file the following documents, each with its distinct filing deadline:
- Form 940, which reports federal unemployment tax, is due by January 31.
- Quarterly Form 941, which reports federal income tax, Social Security, and Medicare taxes, is also expected by January 31.
- Annual Form 944, which reports federal income taxes, Social Security, and Medicare taxes, is due by January 31.
Keeping track of these tax forms and filing deadlines can help your business remain compliant, avoid penalties, and maintain precise accounting records.
ACA Reporting Requirements
When it comes to ACA reporting, being well-informed is your strongest defense. Applicable Large Employers (ALEs) need to provide the IRS with details regarding the health care coverage offered to full-time employees, adhering to guidelines set by the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission.
This step is where Forms 1094-B and 1095-B, as well as 1094-C and 1095-C, come into play. They are your allies in reporting this information and keeping your payroll records in check.
- IRS Form 1094 consolidates the information returns of Form 1095 and provides details about employee eligibility for tax credits.
- IRS Form 1095 reports information about individuals who enroll in a qualified health plan through the Health Insurance Marketplace.
These forms come with a deadline. For paper filers, they must be submitted by February 28, 2024, or March 31, 2024 if you’re filing electronically. Make sure you mark these dates on your calendar to keep your reporting process smooth sailing. If you fail to submit these forms by the deadlines, you could face penalties ranging from $280 to $580 per return.
TIP: Managing compliance isn’t an easy feat. Let your payroll provider navigate and file compliance forms to reduce manual errors and missed deadlines.
5. Update Payroll Policies
As the year-end approaches, it’s essential to review your payroll structure and policies and comply with federal, state, and local labor laws.
Review Payroll Structure and Policies
Evaluating your first payroll structure and policies is vital to ensure accurate tax withholding and adherence to federal regulations. Consider any changes needed for the upcoming year, such as pay-on-demand or paycheck delivery options. Adjustments to your payroll policies can better accommodate your employees’ needs and guarantee an effortless payroll process in the upcoming year.
Don’t forget to stay informed about changes in state and local minimum wage laws or health insurance coverage options, as these factors can impact your employee compensation plans.
A good solution is an automated payroll processing software that can help you run reports to analyze your payroll.
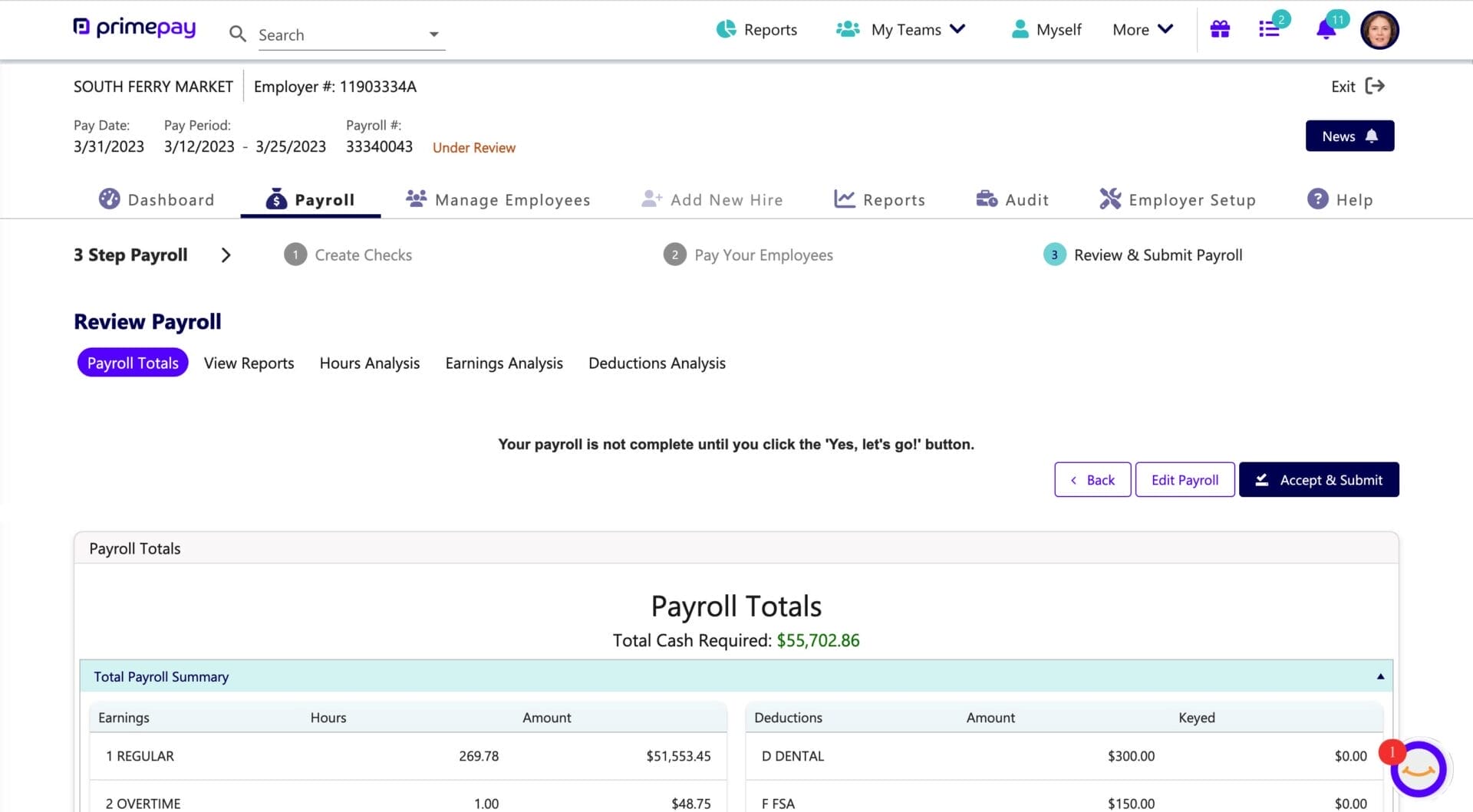
Plan For Holiday Scheduling Challenges
Federal holidays can be a double-edged sword. While they bring joy and relaxation, they can also challenge payroll processing and create some late nights.
By following these steps, you can make sure your payroll tasks remain uninterrupted:
- Set or modify a pay schedule.
- Recognize holiday dates for adjustments.
- Notify employees about changes in advance.
- Update contracts for new hires.
- Smoothly transition from the old to the new plan.
It’s advisable to adjust payroll schedules for holiday periods when the regular pay date coincides with a weekend or a bank holiday. Make these adjustments in advance to ensure punctual payment to employees.
Disseminate Compliance Posters and Regulations
No, those compliance posters aren’t hanging in the office breakroom for light reading. Maintaining compliance with federal, state, and local labor laws is crucial to avoid fines, fees, and potential lawsuits.
Keeping your compliance posters current and staying updated about the latest labor laws can protect your business from potential legal problems and foster a safe and compliant work environment for your employees.
Establish Deposit Schedules
Determining your deposit schedule for the new year is essential to ensure timely tax payments and prevent penalties (is it clear that we want 2025 to be a penalty-free year?). Match your deposit schedule with tax deadlines and adjust as needed to comply with federal and state tax laws.
6. Align Year-End Accounting Procedures and Business Goals
As the year winds down, it’s vital to focus on organizing your accounting records and setting goals for the upcoming year.
Clean Up Accounting Records
One part of your year-end financial review is cleaning up your accounting records. Plan to:
- Clear up any irregularities in outstanding invoices.
- Remove unused or closed accounts.
- Clear any deposited funds to maintain accurate accounting records.
You can ensure a solid financial foundation for the new year by addressing discrepancies in your accounting records.
Besides cleaning up your records, you’ll want to stay updated about any changes in tax laws and regulations that may affect your business. These changes will keep your finances on track (and, once again, avoid those penalties).
Tie Business Goals and Employee Feedback Together
Setting business goals is vital in planning for the upcoming year and driving growth and improvement. Equally important is having your team make these plans become a reality. As your organization develops goals for 2025, consider how you can integrate these goals into performance management. Providing feedback to encourage growth and development is essential.
Offering employee feedback helps ensure your team members know their performance and how they contribute to the organization’s success. Fostering a culture of continuous improvement can contribute to growth and success in the new year.
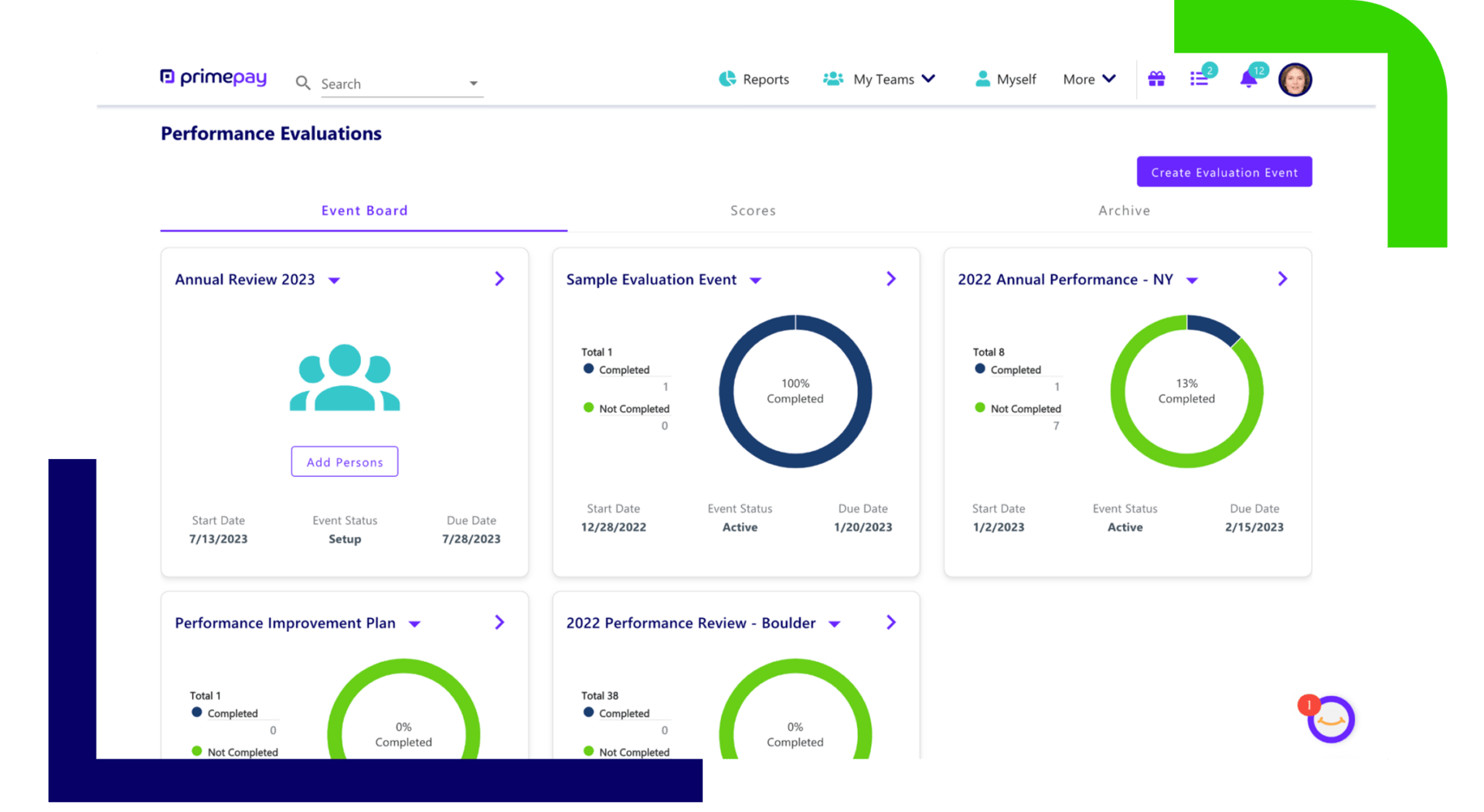
When performance evaluations live in cloud-based software, you provide a more equitable and transparent experience for leadership, managers, and direct reports.
Following a comprehensive year-end payroll checklist can provide a smooth transition into the new year and set your business up for success. With the above steps, you’ll be well-prepared to tackle the challenges and opportunities in the new year.
If you want to add one more item to your checklist, consider switching to a payroll provider that includes human capital management so all your people and compliance needs are in one place.








